Architecture
Schematic overview
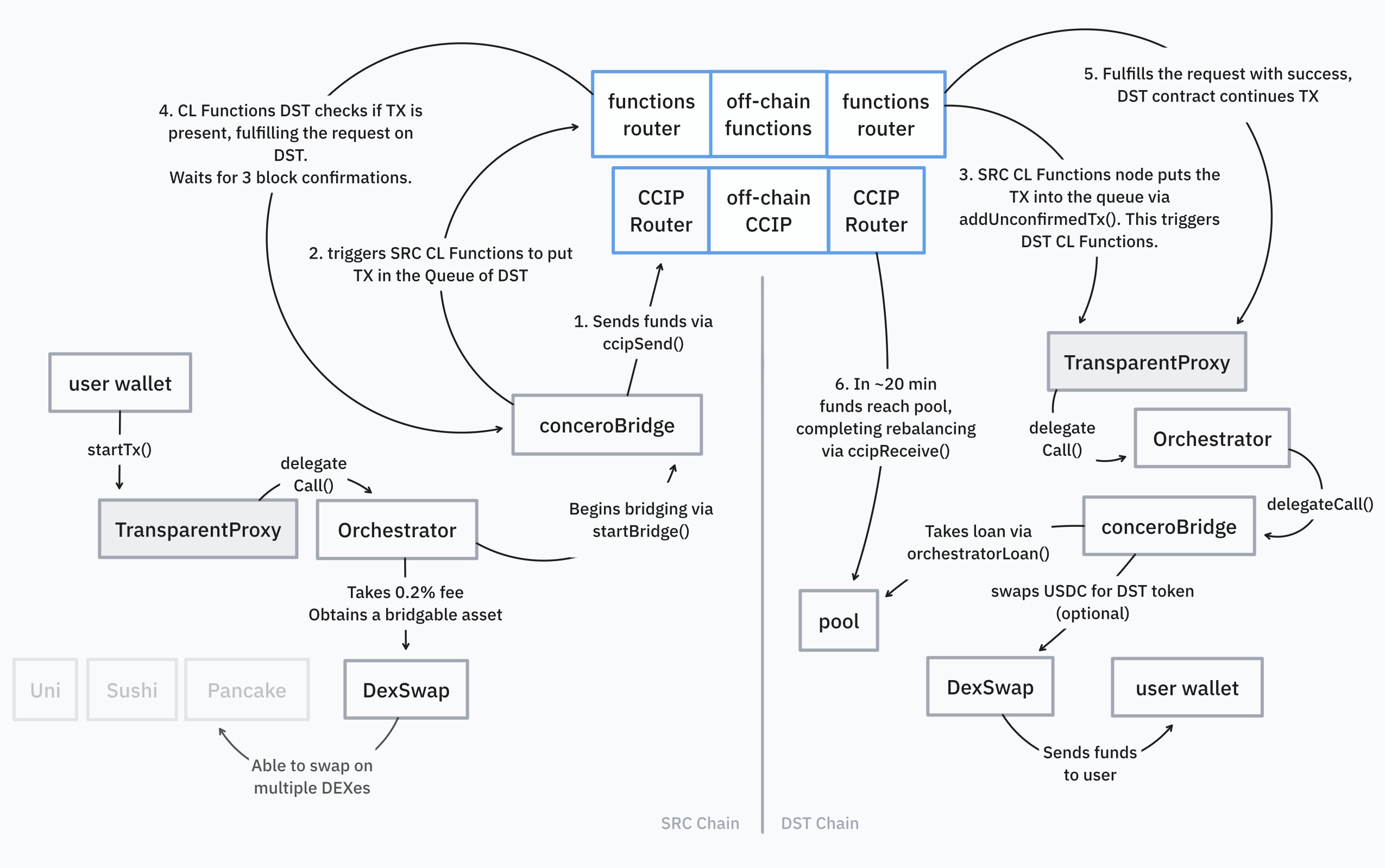
Orchestrator contract (Main entrypoint)
The Orchestrator contract serves as a single entrypoint for users or protocols to interact with Concero cross-chain infrastructure. Responsible for executing the entire transaction on a single chain, allowing a user to perform multiple actions with a single function call.
The actions the Orchestrator handles include:
- Swaps (single or multiple)
- Bridging
- Swaps and bridging
Internal contracts
DexSwap
Serves as an adapter to various decentralised exchanges. Used internally by the Orchestrator in order to perform single-chain swaps.
ConceroBridge
Handles the cross-chain bridging process. Interacts with Chainlink CCIP and Chainlink Functions. Used internally by the Orchestrator in order to perform cross-chain transactions.
Chainlink Functions
Serve the purpose of fast-tracking transactions while CCIP is performing the 24-minute bridging.
SRC Functions
Calls addUnconfirmedTX() function on the DST chain to indicate that a transaction has entered CCIP on the source chain. Uses a private key in DON-Hosted secrets in order to call the function via an allow-listed messenger wallet. The DST contract, which receives such call immediately begins the confirmation process by running an additional set of Chainlink Functions on the destination chain.
DST Functions
The purpose of Destination chain ChainlinkFunctions is to confirm whether the transaction has indeed been submitted to the source chain and has successfully entered CCIP. Using Alchemy, Infura and other RPC providers inside the JS code, it performs an RPC call to read a specific event, which confirms that the transaction is being sent through CCIP.
Additionally, DST functions are responsible for awaiting a certain amount of block confirmations before submitting a successful callback to the DST contract. The minimum of block confirmations depends on the risk factor of each transaction that enters the bridging infrastructure. This itself is a combination of weighted factors such as the amount of transactions, transaction history of the wallet, and any other anomalies that the transaction might have.
Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink CCIP is chosen as a reliable and secure settlement layer due to its complex multi-layered architecture. As soon as funds enter CCIP on the SRC chain, a corresponding event is emitted and Chainlink Functions begin the acceleration process. When the funds have been taken from the liquidity pool in a form of a 24-minute loan, CCIP rebalances that pool by completing the transaction.
Liquidity pools
Liquidity pools are a crucial part of Concero's fast-track solution, as they hold the liquidity necessary to be taken as a loan while CCIP is in process of bridging the assets. As soon as the transaction is confirmed by Chainlink Functions on the DST chain, the Orchestrator contract obtains a loan from the Liquidity pool and proceeds to execute all necessary actions, such as destination chain swaps. This is in order to send the destination asset to the user's wallet.